Our legs help us to wander far afield as we conduct our business and engage in a variety of social activities. However, leg weakness may arise for several reasons and can significantly hamper your ability to complete critical activities of daily living (ADLs).
Vigorous walking is a rigorous sport for the elderly with a lot of leg activity. Therefore, you may be wondering: “How can I find a good physical therapist who works with elderly near me?” Let’s discuss how you can overcome any challenges that you may have with your legs whether you are a gymnast or simply want to get the most out of your legs.
What Causes Leg Weakness?
Leg weakness may manifest as weakness in one or both legs, or as a part of overall weakness in your body. This happens due to the leg muscles losing strength when they are tired, but this condition resolves after resting.
Leg weakness can also occur due to deconditioning or the reversible changes that arise from physical inactivity and disuse. This diminished muscle strength may affect your ability to perform your daily tasks.
However, leg weakness may also arise from the following medical conditions:
Sciatica
Sciatica is a spinal cord condition that causes pinching or compression of the nerves as they exit the spinal cord via the spaces between the backbone’s vertebrae. Sciatica may also cause weakness in a part of the arm or leg, as well as other symptoms like tingling, burning, or pain.
Neuromuscular Diseases
Some of these muscle-weakening illnesses include:
- Myasthenia gravis: An autoimmune neuromuscular condition that causes muscle weakness and debilitating fatigue.
- Multiple sclerosis: A disease that adversely affects the brain and spinal cord leading to muscle weakness, loss of coordination and balance, and other problems.
- Graves disease: This causes the thyroid gland to produce too much hormone which also leads to weight loss, anxiety, quaking, irritability, depression, and mental or physical fatigue.
- Guillain-Barré syndrome: This condition makes the immune system attack the healthy cells in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) resulting in weakness, numbness, tingling, and eventual paralysis.
Thyroid Conditions
Leg weakness may also indicate thyroid conditions:
- Hypothyroidism: This means that your thyroid gland is underactive, or it doesn’t produce sufficient amounts of crucial hormones.
- Hyperthyroidism: In this instance, your thyroid gland is overactive and produces too much of the hormone called thyroxine.
Furthermore, electrolyte imbalances, herniated discs, chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), hypotonia, peripheral neuropathy, neuralgia, polymyositis, and toxins like botulinum, and certain medications may also cause muscle weakness.
Stroke
A stroke may also cause leg weakness, and it is a life-threatening condition. Therefore, you should seek emergency treatment for any leg weakness that suddenly occurs. This is particularly the case if you also experience:
- Blurred or double vision
- Vision changes or vision loss
- Numbness
- Paralysis of a body part
- Severe headaches
- High fever (above 101 degrees Fahrenheit)
- No bladder or bowel control
- Fainting and lethargy
If you experience any of these symptoms, call 911 immediately.
Consequences of Leg Weakness
Some of the consequences include:
Increased Vulnerability to Falling
Leg weakness often makes you more vulnerable to falling. Elderly individuals tend to have weaker muscles and lower flexibility and endurance. This increases their vulnerability to have a serious fall and injure themselves. Even for the young, leg weakness leads to inappropriate muscle contractions that hamper the ability to walk with ease.
Greater Susceptibility to Fractures
A lack of exercise diminishes not only muscle and endurance but also critical bone density. Inactivity (especially in the elderly) leads to osteoporosis which means more fragile bones that break quite easily. For older people with this condition, a sneeze or a sudden movement may lead to a fracture.
Diminished Energy
As your leg muscles get weaker, so do the other muscles in your body. Your heart is one of those muscles that get weaker with inactivity. This leads to a smaller amount of blood circulating with each beat, so your heart has to beat more to circulate the required quantity of blood.
Therefore, sedentary persons tend to have higher heart rates and lower oxygen consumption than those who are active. Your body needs oxygen to convert nutrients into energy, thus lower oxygenation means lower energy. Also, higher heart rates lead to fatigue and poor heart health.
Loss of Independence
The decline in muscle strength means that you won’t be able to complete the necessary daily activities, especially those that require great muscle strength. Therefore, consistent muscle decline may lead to a loss of independence.
Diagnosing Leg Weakness
If you experience leg weakness with no apparent cause, then arrange to see your doctor. They may ask you about the length of time you have experienced this weakness and the muscles that are affected. Be prepared to discuss any other symptoms as well as your family medical history.
Your doctor may also check your:
- Reflexes
- Senses
- Muscle tone
If necessary, you may undergo one or more of the following tests:
- CT scans or an MRI to examine your body’s inner structure
- Nerve tests to determine the health of your nerves
- Electromyography (EMG) to evaluate your nerve activity
- Blood tests to check for any infections or other issues
Dealing With Leg Weakness: Treatment Options
Once your doctor discovers the underlying reason(s) for your leg weakness, they can recommend the right treatment. Your treatment plan will depend on the cause of your ailment and its severity.
Some of the treatment options include:
Physical Therapy
Physical therapists may suggest exercises to make your life better – especially if you have MS or ALS. In the former case, a physical therapist may recommend progressive resistive exercise for muscle strengthening. For a patient with ALS, they may prescribe stretching and range of motion exercises to alleviate stiff muscles.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy focuses on exercises that build your upper body strength. They will also help you to use assistive devices and tools (if necessary) to master your activities of daily living (ADLs). Occupational therapy is quite useful especially during stroke rehabilitation. In such instances, an occupational therapist may recommend exercises to strengthen the weakened side of the body and improve motor skills.
Medication
Over-the-counter (OTC) painkillers like ibuprofen and acetaminophen help manage painful conditions such as peripheral neuropathy, CFS, and neuralgia.
Thyroid hormone replacement is often used to relieve the symptoms of hypothyroidism. The standard treatment protocol includes levothyroxine (Levoxyl, Synthroid), which is a synthetic thyroid hormone.
Diet Changes
Modifying your diet may help you address any electrolyte imbalances. Your physician may also recommend that you take supplements like calcium, magnesium oxide, or potassium oxide.
Surgery
Surgery may be the core treatment option for certain conditions (for example, a herniated disc or hyperthyroidism).
Treatment and Therapy Options for Muscle Weakness
The underlying causes and symptoms of your muscle weakness will determine the treatment and therapy you need:
- If the condition arose from overexertion or injury, then it can be mitigated after a recovery period. Regular exercise will improve and strengthen your muscles.
- Making dietary changes and taking supplements will help to resolve any leg weakness caused by following an unhealthy diet.
- After any infectious disease, you will often regain your muscle strength.
- Medication may also mitigate specific types of muscle weakness (like myasthenia gravis).
Furthermore, muscle weakness may arise from:
- An accident or surgery (for example, cruciate ligament and meniscus damage, shoulder, hip, spinal disc, and back issues, peripheral nerve damage, and incomplete tetraplegia leading to muscle atrophy)
- A disorder after suffering a stroke
- A symptom of a neural or muscular disorder (for example, MS)
Treatments may alleviate some of the symptoms, but not resolve the cause of the disorder. The previously discussed scenarios may make such persons good candidates for symptomatic therapies for muscle weakness. These therapies are:
Physiotherapy
These are regular exercises that may or may not use equipment to build and strengthen muscles. The exercises are conducted under the instructions of a licensed physiotherapist. Further muscle strengthening may also mean combining physiotherapy and supplementing them with physical treatments.
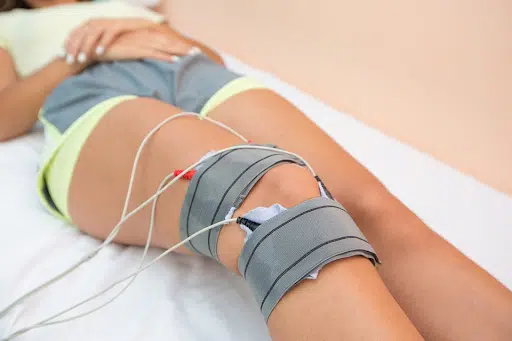
Electrotherapy
Whenever muscles are inactive, such as in cases of illness, post-accident, or immobility, this process may be delayed or stopped using electrically-generated pulses to strengthen the muscles.
Electrotherapy also improves blood flow, endurance, and mobility. These electrical signals strengthen your muscles by contracting them. The signals that trigger these muscle contractions are transmitted via electrodes attached to your skin.
This therapy helps you avoid reduced muscle strength and imbalance. Combining preventive treatment and electrotherapy helps you avoid secondary orthopedic injuries and shorten your recovery time, which as a gymnast, is ideal.
Electrotherapy should be regularly used. The good news is that it’s quite easy to use some electrotherapy devices at home with detailed, expert instructions.
At-Home Physical Therapy Exercises for Leg Strengthening
Regardless of the reasons for needing physical therapy, it has improved many lives. While you will need to complete your standard physical therapy sessions, it is also helpful to perform leg exercises at home.
Regaining your leg strength is a critical part of your recovery. Initially, you will target the major muscle groups within your leg. There are three main areas of your leg that your exercises should focus on to improve your leg strength. Always check with your physician or physical therapist to find out what exercises are acceptable for your unique case.
Let’s discuss these exercises in more detail:
Glute Sets
It’s easy to exercise your glutes and strengthen your hips. These exercises improve your blood circulation to your hips and legs. Here are the steps:
- Lie flat on your back and then bend your knees at a 15-degree angle. You may want to lie on an exercise mat to be comfortable.
- Slightly raise your buttocks off the ground and squeeze/tighten the muscles in your buttocks.
- Hold for about five seconds.
- Then relax your buttocks.
- Repeat three sets (containing 10 repetitions each) every day.
You can choose to increase or decrease these repetitions depending on your level of tolerance. If you experience intense pain, stop this exercise and contact your medical professional.
Hamstring Sets
The hamstring is important as it helps you to bend your knee and extend your hip backward. Therefore, it’s critical to strengthen your hamstrings to aid your recovery process and get you back to walking easily and pain-free. This is a simple hamstring set that most people can do:
- Lie on your stomach on a comfortable, stable surface (such as an exercise mat).
- Raise your leg backward at a height of about 10 to 12 inches.
- Hold for 5 seconds.
- Slowly lower your leg back to the original position.
- Complete two or three sets every day. Each set contains 10 to 15 repetitions.
Quad Sets
The quadricep muscles consist of four (quad) muscles along the front end of the thigh. These muscles contract in unison to lift your hip and extend your knee. While there are a variety of quad strengthening exercises, here’s a simple version you can do at home:
- Lie flat on your back on an exercise mat for comfort.
- Bend the knee of your uninjured leg to a 90-degree angle while keeping the weaker leg straight and flat on the mat.
- Slowly lift your weaker leg until it is approximately 12 inches above the ground.
- Hold for 5 seconds.
- Slowly lower your leg back to the ground.
- Complete two or three sets every day with 10 to 15 repetitions in each set.
These are a few instances of leg-strengthening exercises you can perform at home to increase the speed of your recovery. There are many other exercises that you can do to strengthen your glutes, hamstrings, quadriceps, and other vital areas of your lower body. Your physical therapist can also create a custom exercise program for you to complete at home.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Some of these questions are:
How Can I Improve My Leg Strength?
You can complete:
- Aerobic exercises like walking, stationary cycling, and water aerobics are great low-impact ways to improve your blood flow and muscle strength.
- Heel raises
- Calf stretches
- Hamstring stretches
- Tandem balance exercises
What Are Some of the Leg Workouts That You Can Complete?
These include:
- Squats: 3 sets with 10 reps each
- Lunges: 3 sets with 10 reps each
- Pistol square or single-leg box squats: 3 sets with 10 reps on each side
- Good mornings: 3 sets with 10 reps each
- Donkey kicks: 3 sets with 10 reps on each side
- Side lunges: 3 sets with 10 reps on each side
- Calf raises: 3 sets with 10 reps each
- Glute bridges: 3 sets with 10 reps each
What Deficiency Leads to Leg Weakness?
A lot of muscle weakness in your leg may arise from vitamin D deficiency. This leads to a feeling of heaviness in your legs, easy fatigue, difficulty climbing stairs, and getting up from a seated position. Vitamin D supplementation is an easy solution.
What Foods Strengthen Your Leg Muscles?
While this list isn’t exclusive, some foods are:
- Yogurt (most brands are vitamin D-fortified and you could get up to 30% of your daily calcium intake).
- Milk
- Salmon and tuna
- Spinach
- Fortified foods
What Does It Mean When Your Legs Get Weak?
If you begin to feel weak or light-headed, you may have hypoglycemia. If your blood sugar is low, then you may experience weakness or tremors in your arms and legs.
Can Heart Issues Lead to Leg Weakness?
Many Americans suffer from heart conditions that may be alleviated with exercise and weight loss. However, exercise may lead to leg weakness and, this, in turn, can make further exercise difficult.
What Causes Leg Weakness in Seniors?
The elderly tend to have diabetes and atherosclerosis which hamper easy blood circulation. Smoking, a sedentary lifestyle, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol may cause poor circulation. Minimize extreme lower body weaknesses by elevating your legs when you are sitting or lying down.
How Do I Find a Good Physical Therapy Institution?
Choosing to locate a good physical therapist who works with gymnasts near me has many benefits. If you need an experienced physical therapist and you are in the Shelton, CT area, then contact Moving With Hope. Our team of medical experts will coordinate with your physician to give you the best healthcare. Let’s work together to help you regain your health and proper leg function.





Comments 2
whats up
I couldn’t refrain from commenting. Very well written!